Types of Wi-Fi authentication:-
Wi-Fi
Authentication can be done by using Open authentication, WEP, WPA & WPA2 or
may be some time MAC based authentication is also used. In Open authentication
as per name suggest there is no authentication required it is like open for
public to connect, this type of authentication is least secure. Second one is
Wired Equivalency Protocol or WEP this type of authentication we use Shared Key
for Authentication. A WEP key is composite of either 40bit or 128bit
encryption, but still this type of authentication is not very much secured.
WPA/WPA2 shared key authentication is very much secure than WEP the also use
shared key authentication as WEP but the difference is in the WEP Access-Point
send password to client machine in encrypted form as a challenge string then
client send it back by solving the challenge string, but in the WPA/WPA2 client
send the password string to the access-point and then access-point, so unlike
password in not stored in client machine. In MAC-based authentication client is
authenticated by using its MAC address this type of authentication is not
secure or maybe I can say it is as weak authentication as open authentication.
In WEP
shared key authentication
Now we will
start with WEP authentication bypass I will do it step by step so it will be
easy for you to understand. Click Images to understand the command in proper
way.
How does it work?
As I have
explained above that WEP send you key in encrypted format. All we need is to
decrypt it to do that we capture some data. Then by analyzing them we find out
encryption method for that key and we can decrypt it easily.
I am going to Backtrack, you can use any other OS also but make sure to install aircrack-ng software in that.
Step1:-
First of all check The name of your wireless interface card and also check that
it is IEEE 802.11bgn almost all new card are 802.11bgn.
To check iwconfig

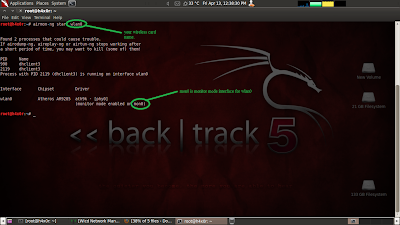
Step2:- Now
that we know name of our wireless interface( in my case it is wlan0) we can
start it in monitor mode, monitor mode is essential for attack. To do so give
command
airmon-ng
start wlan0
after that
it will enable the interface in monitor mode in my case it is mon0. That is my
monitor interface.
Step3:- now
than we are all set with interface so we will check all available Access-Point
and client associated with it. To check that
airodump-ng mon0
Press
Ctrl+c to stop the command once you got
the list of all available Access-Point.
After
giving that command it will show you all available Access-point and client
associated with it. Beside this information it also show you type of authentication
Access-Point is using and the ESSID which is the name of Access-Point. BSSID is
the Mac Address of the Access-Point.Ch is channel on Which Access-Point is
working. In this tutorial we will see how to bypass WEP type of encryption
only.
Step4:-
Time to capture some data, to do so give command:-
airodump-ng –c [channel] –bssid [bssid] –w
[file name to store data] mon0
now it will
start capturing and storing all data into the file name you have given to it.
Note:-
don’t stop the command or close the terminal
Step5:-
open a new terminal. If data are note increasing quickly then you can increase
it by yourself by transmitting fake data. To do that give command:-
aireplay-ng -3
–e [essid] mon0
or
aireplay-ng -3 –b [bssid] mon0
it will
start sending fake data and will increase your captured data.
Don’t close
this terminal also.
Step6:-
open new terminal. Now once we got enough data we can start out attack. First
locate the file in which you stored your data(to locate type ls command) then start attack.
aircrack-ng
[filename in .cap formate]
now the attack has started it can take time.
As we see
it didn’t work with 3000 IVs, so it will try after getting 5000 IVs you don’t
have to start the attack again it will start as soon as it will get 5000 IVs.
IVs increase as per Data.
Got
the password in clear text form you can login using that password.








No comments:
Post a Comment